5 Stages of Business Life Cycle: A Beginner’s Guide
Small businesses vary in size and how much they can grow. They
- Work on their own,
- Organize themselves in different ways, and
- Use different ways to manage things.
Businesses, ranging from local dry cleaners to high-tech companies, go through different stages of growth. Researchers have broken down these growth phases into 5 key stages.
But, if we take a closer look, we find that all businesses (giants or small) deal with similar issues at similar growth stages. We can organize these common points into a framework.
This helps us understand businesses better – their nature, characteristics, and problems.
It’s important to know the main steps in a business’s life cycle to make sure your business doesn’t face problems. You need to figure out which part of the cycle of business your company is in. This will guide how you run things and plan for the future.
In this post, we’ll talk about how a regular business goes through different stages. Starting from the idea to when it slows down. We’ll also see how the business life journey is not the same as business growth.
We’ll give examples and discuss the important things to focus on during each stage.
Let’s get started!
But first, let’s understand the business life cycle meaning.
What Is The Business Cycle
Business Cycle Meaning
In business, the “cycle” means the repetitive pattern of stages that companies go through. From starting up to growing, stabilizing, and sometimes declining.
It’s the journey a business takes, with each stage having its challenges and opportunities.
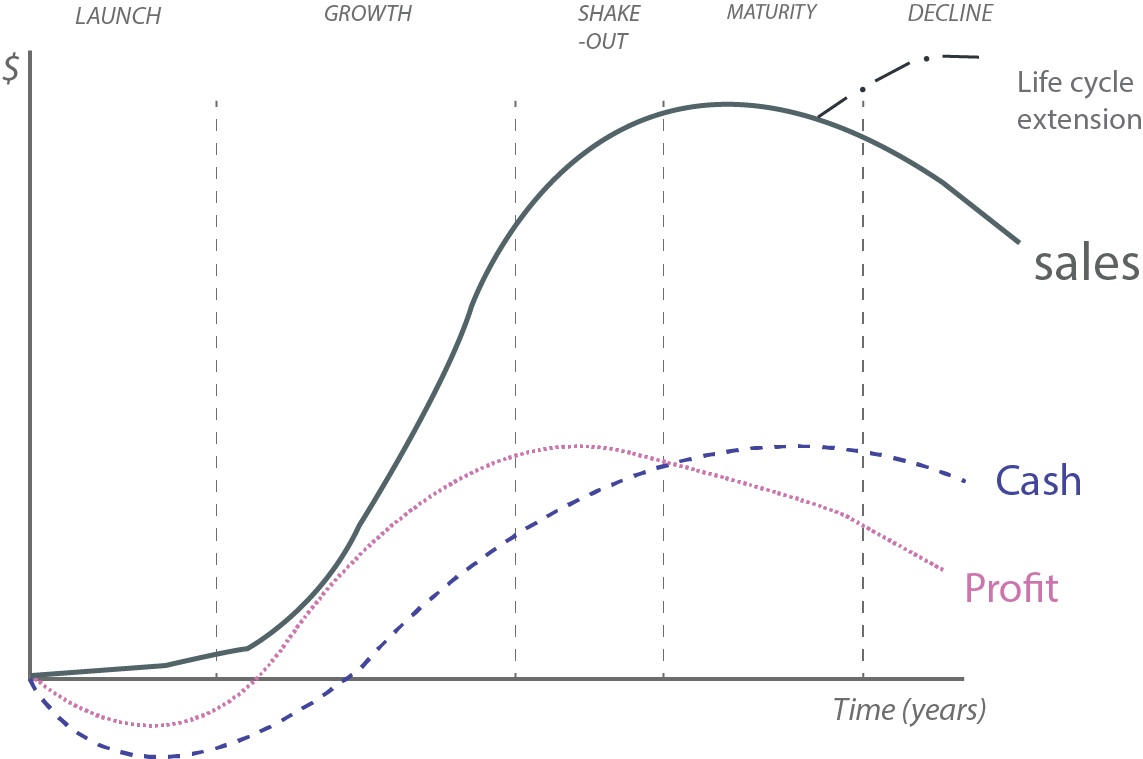
The business life cycle is how a business grows and changes over time. It has five stages: launch, growth, shake-out, maturity, and decline.
Understanding this cycle helps owners make better decisions for the present and future of their businesses.
This article will use three financial metrics – sales, profit, and cash flow – to explain each stage. Following are the 3 money-related metrics to understand at each business stage:
- Sales: How much the business sells.
- Profit: How much profit it makes.
- Cash Flow: How much cash it has.
Business Cycle Diagram
5 Stages In Business Life Cycle | A Closer Look
Every business goes through different stages in its life. If you want your small business to succeed, you must understand
- How does each stage work?
- What to do during those stages to win?
Here are the 5 key stages of a business life cycle:
Stage 1: Start-Up & Launch
In the first stage, every business introduces new products or services. They focus on getting customers and delivering products or services.
In this phase, sales are low but slowly increasing. Businesses focus on marketing to their target customers.
However, they often face losses because revenue is low, and start-up costs are high. Profits come later in the business life cycle after sales have grown.
In this phase, research and development play a crucial role. Owners
- Plan the business,
- Decide on products and services,
- Calculate costs, and
- Establish a business model.
A strong business model is essential for securing financing and successfully launching the company.
At launch, when sales are low, the business risk is high. Companies can’t borrow much because their business model is unproven. As sales increase, the ability to borrow also goes up.
Stage 2: Growth
Companies set themselves apart in the market during this stage.
Once a business proves it’s viable, it moves to survival mode. The main challenge shifts to balancing revenues and expenses. Owners must generate enough cash to break even and cover necessary expenses.
During the growth phase, companies see rapid sales growth. Profits start coming in after reaching the break-even point. Cash flow becomes positive, showing more money coming in than going out.
Business owners,
- Focus on expanding,
- Building client relationships,
- Increasing investments, and
- Seeking capital.
With booming sales, business risks decrease, and borrowing ability increases. Profits and positive cash flow show that the company can repay debts. Some may take on debt or consider going public.
During this stage, the focus should be on challenges that could slow down growth.
Stage 3: Shake-out
In the shake-out phase, sales keep increasing, but not as fast. This could be because the market is getting full or new competitors are joining.
Sales increase, but profit starts to decline due to increased costs. Cash flow, however, goes up and surpasses profit.
During the shake-out, sales peak, but debt financing increases. Companies prove they can repay debts, and business risk keeps going down.
Stage 4: Maturity
In the maturity phase, sales slowly decrease, and profit margins get smaller. Cash flow stays steady, and major spending decreases. As companies mature, sales decline, but now there’s less business risk. The most stable businesses easily get debt capital.
The business is doing well, with a great team and steady growth. During this stage, owners decide whether to expand the business or maintain stability.
There could be chances to buy other businesses, and owners can think about things like starting new parts of the business. They can use the money to grow more or choose to sell what they own.
Some businesses extend their life cycle by reinventing themselves. By investing in new technologies and entering new markets.
Stage 5: Innovate or Decline
In the final stage, sales, profit, and cash flow all decrease. If there are consistent drops in revenue during the maturity stage. The company is in decline.
Business owners need to
- Innovate,
- Reinvest, or
- Sell the business to turn things around.
Selling during this stage can be more challenging and less rewarding.
Companies have to adapt to changes to continue growing. But if the business keeps on declining and sales keep on dropping fast. Then this shows the business couldn’t adapt. At this stage, securing debt becomes difficult as lenders perceive higher risk.
Hence, such companies have to leave the market.
Business Growth Stages Help Avoid Future Problems
Understanding these growth stages helps small business owners predict challenges and make informed decisions to ensure their business’s success.
The framework also benefits consultants in finding problems and advising solutions suitable for each stage of development.
Business Life Cycle Case Studies
Here are a few major examples and case studies of businesses going through different stages of the life cycle:
1st Case Study: Blockbuster
- Startup Phase: Blockbuster dominated the video rental market with physical stores, establishing itself as a go-to for movie rentals.
- Growth Phase: As competition grew, Blockbuster faced challenges to balance revenue and expenses, surviving the evolving market.
- Success & Shake-Out Phase: Blockbuster succeeded, becoming a household name for movie rentals but struggled to decide on growth strategies.
- Maturity Phase: The rise of online streaming posed challenges, and Blockbuster struggled to adapt, leading to a decline in its business.
- Decline Phase: Failing to innovate and embrace new trends. Blockbuster declined, eventually leaving the market.
2nd Case Study: Kodak
- Startup Phase: Kodak enters the scene, dominating photography with film and cameras, capturing memorable moments.
- Growth Phase: Thriving in the film era, Kodak faces challenges as digital photography emerges, testing its survival.
- Success & Shake-Out Phase: Kodak’s success in the film industry reaches its peak, but signs of decline emerge with the shift to digital technology.
- Maturity Phase: Unable to adapt, Kodak faces a decline, struggling to take off in the digital age.
- Decline Phase: Failing to innovate and adapt, Kodak experiences a significant decline, eventually filing for bankruptcy.
3rd Case Study: Netflix
- Startup Phase: Netflix emerged, offering DVD-by-mail services as a convenient alternative to traditional video rentals.
- Growth Phase: Adapting to consumer needs, Netflix transitioned to streaming, ensuring survival and growth in a changing market.
- Success & Shake-Out Phase: Netflix became a streaming giant, surpassing Blockbuster, and setting the standard for online entertainment.
- Maturity Phase: Rapid expansion in the streaming market marked Netflix’s take-off, solidifying its dominant position.
- Innovation Phase: Consolidating gains, Netflix diversified its content and became a leader in the entertainment industry.
4th Case Study: Amazon
- Startup Phase: Amazon began as an online bookstore, quickly expanding into diverse product categories.
- Growth Phase: Introducing services like Prime, AWS, and Kindle, Amazon thrived in the evolving e-commerce and tech landscape.
- Success & Shake-Out Phase: Amazon’s success lay in its global presence, and it continued to innovate with services like Prime Video and Alexa.
- Maturity Phase: Amazon’s take-off involved rapid expansion and diversification, establishing itself as a global giant.
- Innovation Phase: Diversifying into streaming (Amazon Prime Video) and AI (Alexa), Amazon solidified its market position, through innovation.
5th Case Study: Apple Inc.
- Startup Phase: Founded in a garage, Apple focused on personal computers, marking the start of its journey.
- Growth Phase: Introducing iconic products like the iPod and iPhone, Apple thrived, balancing revenues and expenses.
- Success & Shake-Out Phase: Apple reached success, becoming an industry leader with a strong market presence and a focus on innovation.
- Maturity Phase: The launch of groundbreaking products propelled Apple’s take-off, leading to rapid expansion.
- Innovation Phase: Diversifying into various industries, Apple maintained innovation, solidifying its position as a tech giant.
6th Case Study: Tesla
- Startup Phase: Founded by Elon Musk, Tesla focused on electric cars and renewable energy, marking its entry into the automotive industry.
- Growth Phase: Tesla’s survival involved successful electric vehicles, and establishing its presence in the market.
- Success & Shake-Out Phase: Tesla’s success continued with advancements in autonomous driving and expansion into energy storage and solar products.
- Maturity Phase: Introducing new vehicle models marked Tesla’s take-off, maintaining growth and innovation.
- Innovation Phase: Tesla achieved resource maturity by consolidating financial gains and maintaining its position as a leader in electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions.
Final Takeaway
In the world of business, the “life cycle” is the journey every company goes through. From start-up, all through the challenging stages of growth, stability, and sometimes decline.
Each “life stage” presents unique opportunities and problems. Just like the “cycle of life” in nature, businesses must adapt and evolve.
Therefore, understanding this cycle is important for business owners. It guides them in making smart decisions. Making sure their companies thrive at every turn in the cycle of business life.
Achieve Business Success with Expert Tax Accounting in Australia!
Looking to fuel your company’s growth?
Our expert tax accounting services in Australia are here to assist. We provide valuable guidance to propel your company through the ups and downs of the business life cycle.
Whether you’re in the startup phase, aiming for growth, or ensuring stability, we provide expert solutions.
Ready for financial success?
Don’t miss out! Let’s discuss your business goals and create a roadmap for your financial success.
Take the first step – set up a consultation today!